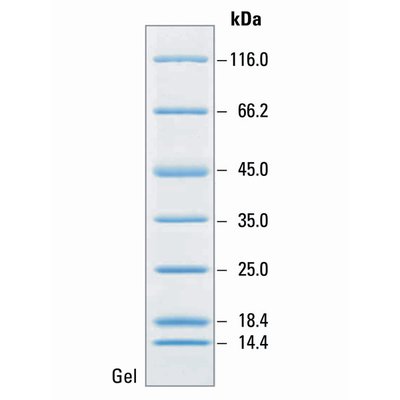
Protein Molecular Weight Markers
Browse our range of specific-mass protein markers for use as approximate sizing standards in protein gel electrophoresis (e.g. in SDS-PAGE). Choose between individual or ladder series markers, from broad size ranges, or preformulated, prestained or unstained versions depending on your needs.
Useful Links
Save Now - Exclusive Deals
Product Code 4529982
Product Code 3667607
Product Code 7225563
Product Code 3667601
Product Code 10755869
Product Code 10420315
Product Code 18656251
Product Code 16592532
Product Code 10640504
Product Code 11574986
Product Code 10413442
Product Code 10377952
Must Have
Product Code 11882114
Product Code 10154962
Product Code 10174502
Product Code 7225574
Product Code 11558636
Product Code 4924116
Product Code 11872124
Product Code 10273723
Complete Your Order - Great Deals
Product Code 15314604
Product Code 10038760
Product Code 4528904
FAQ
A protein molecular weight marker, also known as a protein ladder or protein standard, is a mixture of proteins with known molecular weights that are used as reference points in gel electrophoresis. These markers are essential for estimating the molecular weights of proteins in a sample by comparing their migration distances during electrophoresis. Key features of protein molecular weight markers are:
- Known Molecular Weights: The marker contains proteins with precisely determined molecular weights, often ranging from a few kilodaltons (kDa) to several hundred kDa
- Pre-stained or Unstained: Pre-stained markers are pre-labeled with dyes, allowing for easy visualization during and after electrophoresis. They are useful for monitoring the progress of the run and for immediate estimation of protein sizes. Unstained Markers are are not dyed and typically require staining after electrophoresis (e.g., with Coomassie Brilliant Blue or silver stain) to be visualized
- Broad Range or Specific Range: Broad range markers cover a wide range of molecular weights, making them versatile for various applications. Specific range markers are designed to cover a narrower range of molecular weights, providing higher resolution in specific size ranges
Applications
- SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis): Protein molecular weight markers are commonly used in SDS-PAGE to estimate the molecular weights of denatured proteins. The SDS gives proteins a uniform negative charge, allowing them to be separated based on size
- Western Blotting: After transferring proteins from an SDS-PAGE gel to a membrane, molecular weight markers help identify the positions of target proteins during immunodetection
- Native PAGE: In native PAGE, where proteins are not denatured, molecular weight markers help estimate the sizes of proteins in their native, functional states
How to Use Protein Molecular Weight Markers
- Mix the protein marker with an appropriate loading buffer, if required. Load the marker into one or more wells of the gel alongside your protein samples
- Electrophoresis: Run the gel under the appropriate conditions (e.g., voltage, time). After electrophoresis, visualize the proteins using appropriate staining or detection methods. Compare the migration distances of the proteins in your samples to the marker bands to estimate their molecular weights
Using protein molecular weight markers can present several challenges that may affect the accuracy and reliability of your results in gel electrophoresis and related techniques. Here are some common challenges:
- Inconsistent Band Migration: Variations in gel composition or running conditions. To overcome this, consider standardizing gel preparation and electrophoresis conditions
- Poor Resolution: Incorrect gel concentration or protein overloading. Make sure to use appropriate gel concentration and avoid overloading wells
- Visualization Issues: Inadequate or uneven staining; pre-stained markers might lack resolution. To avoid this issue, follow proper staining protocols and consider using unstained markers with post-staining
- Marker Compatibility: Incompatibility with detection methods or sample types
- Batch-to-Batch Variability: Variability between different marker batches affecting reproducibility
By addressing these challenges with standardized practices and careful selection of markers, you can improve the accuracy and reliability of your protein molecular weight estimations.
When selecting protein molecular weight markers, it's important to consider several factors to ensure they meet the specific needs of your experiment and provide reliable results. Here are five key considerations:
Molecular Weight Range
- Ensure the marker covers the molecular weight range relevant to your proteins of interest. If your proteins are small, a marker with a lower range is needed, whereas for larger proteins, a marker with a higher range is required.
- Consider the resolution within the molecular weight range. Some markers provide closely spaced bands for better resolution of proteins in a specific range.
Type of Visualization
- Pre-stained markers are pre-labeled with dyes, allowing for immediate visualization during and after electrophoresis. They are useful for tracking the progress of the run and for quick size estimation.
- Unstained markers require post-electrophoresis staining (e.g., Coomassie Brilliant Blue or silver stain) to be visualized. They are often used when precise quantification or specific staining protocols are needed.
- Dual-color or multi-color markers contain proteins labeled with different colors, providing more detailed reference points and aiding in the accuracy of molecular weight estimation.
Compatibility with Detection Methods
- Ensure the marker is compatible with Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining if this is your chosen method.
- Check compatibility with silver staining if this is your chosen method, which is more sensitive but may not work well with all markers.
- If you plan to use the marker for Western blotting, ensure it is compatible with the detection method (e.g., chemiluminescence, fluorescence) and that the marker proteins can be detected alongside your target proteins.
Accuracy and Reproducibility
- Choose markers known for their batch-to-batch consistency to ensure reproducible results across different experiments.
- Select markers that produce sharp, well-defined bands for accurate molecular weight estimation.
Ease of Use and Cost
- Consider how easy the marker is to prepare and load. Pre-mixed markers with loading buffer can save time and reduce preparation errors.
- Balance the cost of the marker with your budget while ensuring it meets the necessary quality and performance criteria. Higher-quality markers may be more expensive but can provide more reliable and accurate results.