Acrylamide Electrophoresis Gels
Acrylamide electrophoresis gels are designed for protein and nucleic acid electrophoresis. Achieve optimal separation of your target proteins with gels available in various types, densities, sizes, well configurations, and buffer formulations, suitable for both native and denaturing PAGE applications.
Useful Links
Save Now - Exclusive Deals
Product Code 200062254
Product Code 7237806
Product Code 7164743
Product Code 7164745
Product Code 7164741
Product Code 7237810
Product Code 7237819
Product Code 7182048
Product Code 7237822
Product Code 7237803
Product Code 7237823
Product Code 7237813
Must Have
Product Code 7237830
Product Code 7237821
Product Code 7237825
Product Code 7237818
Product Code 7237831
Product Code 7224320
Product Code 7224325
Complete Your Order - Great Deals
Product Code 11529166
Product Code 11549166
Product Code 10424012
FAQ
In gel electrophoresis, acrylamide is used to form a polyacrylamide gel, which serves as a matrix through which molecules such as proteins or nucleic acids can be separated based on their size and charge. Here are the key roles and functions of acrylamide in gel electrophoresis:
Gel Formation
Acrylamide, in combination with a cross-linker (usually N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide), undergoes a polymerization reaction to form a polyacrylamide gel. This gel consists of a network of long polymer chains cross-linked to each other, creating a porous structure.
Controlling Pore Size
The concentration of acrylamide and the ratio of acrylamide to bisacrylamide determine the pore size of the gel. Higher concentrations of acrylamide create smaller pores, which provide higher resolution for separating smaller molecules. Conversely, lower concentrations create larger pores, suitable for separating larger molecules. Typical acrylamide concentrations range from 3-20%, with lower percentages being used for larger molecules and higher percentages for smaller molecules.
Resolution and Separation
The polyacrylamide gel acts as a molecular sieve. Smaller molecules move more easily through the pores and thus migrate faster, while larger molecules are impeded and migrate more slowly. This size-dependent migration allows for the separation of molecules based on their size.
In protein electrophoresis, such as SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis), proteins are denatured and coated with SDS, which gives them a uniform negative charge. The polyacrylamide gel then separates the proteins primarily by size.
Stability and Versatility
Polyacrylamide gels are chemically stable and can be used for a variety of electrophoretic techniques, including native PAGE (where proteins are not denatured) and denaturing PAGE (such as SDS-PAGE). The gels can be cast into various thicknesses and formats, including slab gels and tube gels, depending on the experimental requirements.
Agarose and acrylamide gel electrophoresis are two common techniques used to separate molecules, typically nucleic acids and proteins, based on their size and charge. The main differences between the two are:
Gel Composition
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis uses agarose, a polysaccharide extracted from seaweed. The gel is cast by dissolving agarose powder in a buffer solution and allowing it to cool and solidify.
Acrylamide Gel Electrophoresis uses polyacrylamide, formed by the polymerization of acrylamide monomers with a cross-linker (usually bisacrylamide). The polymerization process is initiated chemically.
Pore Size
Agarose has relatively large pores, making it suitable for separating larger molecules such as DNA fragments (typically ranging from 100 bp to several kb). Acrylamide has smaller, more uniform pores, which are suitable for separating smaller molecules such as proteins and small nucleic acids (typically ranging from 5 bp to
1 kb).
Resolution
Agarose provides lower resolution due to larger pore size, ideal for separating large DNA fragments but less effective for small fragments or proteins. Acrylamide provides higher resolution due to smaller pore size, making it ideal for distinguishing between proteins or small nucleic acid fragments with small differences in size.
Applications
Agarose is commonly used for DNA and RNA electrophoresis, especially for routine analysis such as checking the size of PCR products, restriction digests, and RNA integrity. Acrylamide: is commonly used for protein electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and high-resolution DNA sequencing gels, as well as for separating small nucleic acid fragments.
Preparation and Handling
Agarose is easier and safer to prepare, as it does not involve toxic chemicals. Simply dissolve in buffer, heat, and pour into a mold. Acrylamide is more complex and requires careful handling due to the toxicity of acrylamide monomers. Polymerization must be carefully controlled, usually with the addition of TEMED and ammonium persulfate.
Running Buffer
Agarose often uses TAE (Tris-acetate-EDTA) or TBE (Tris-borate-EDTA) buffer. Acrylamide typically uses Tris-Glycine-SDS buffer for protein electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
When selecting acrylamide electrophoresis gels, there are several important factors to consider to ensure optimal separation and analysis of your samples. Here are five key considerations:
- Acrylamide Concentration: the concentration of acrylamide in the gel determines the pore size, which directly affects the resolution and range of molecule sizes that can be separated. Lower concentrations (e.g., 5-8%) are used for larger proteins or nucleic acids, while higher concentrations (e.g., 10-20%) are used for smaller proteins or nucleic acids. Gradient gels, which have varying acrylamide concentrations, can be used to separate a wide range of molecule sizes in a single gel.
- Type of Gel (Denaturing vs. Native): Denaturing Gels are used to separate molecules based on size alone, with the use of denaturing agents like SDS (SDS-PAGE for proteins) or urea (for nucleic acids). These gels disrupt secondary and tertiary structures, giving molecules a uniform charge-to-mass ratio. Native Gels are used to separate molecules based on their native conformation, charge, and size. These gels do not contain denaturing agents, preserving the natural structure and function of the molecules.
- Buffer System: the choice of buffer can influence the resolution, running conditions, and the types of molecules best separated by the gel. Common buffer systems include Tris-Glycine for SDS-PAGE and Tris-Borate-EDTA (TBE) or Tris-Acetate-EDTA (TAE) for nucleic acids. Ensure the buffer system is compatible with the type of electrophoresis being performed and the molecules being analyzed.
- Gel Thickness and Format: the thickness of the gel can affect the resolution and the amount of sample that can be loaded. Thicker gels can accommodate larger sample volumes but may require longer run times. The format of the gel (e.g., slab gels, gradient gels, or tube gels) should be selected based on the specific application and the equipment available.
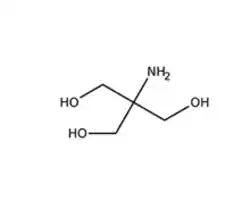
- Polymerization and Gel Preparation: consider the polymerization process and the handling of acrylamide, which is a neurotoxin in its monomeric form. Ensure proper safety protocols are followed during gel preparation.
The polymerization conditions (e.g., the concentration of TEMED and ammonium persulfate) should be optimized to produce a consistent and uniform gel matrix.